Ad Code
Categories
Most Popular
Work, Energy and Power | Physics, Definition, Types, Formulas, Simple explanation |
The terms work, energy and power are frequently used in everyday language. In physics, however the word, 'Work' converse a definite and precise meaning.
'Energy' is capacity to do work. In physics, the term energy is related to work. The word 'Power' is used in everyday life With different shades of meaning.
Work
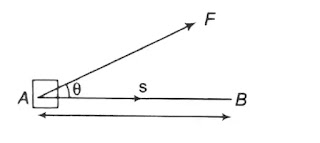
When a body is displaced by applying a force on it, then work is said to be done.
If a body is displaced by a distance s on applying a force F on it, then the work done
W = F • s
It is a scalar quantity.
If there is an angle θ between the direction of force and direction of displacement, then work done
W = Fs cos θ
Thus, we can see that work is the scalar product of force and displacement.
So, if θ is acute angle, then work is positive. If θ is right angle then work is zero. If θ is obtuse angle, then work is negative. In CGS system unit of work is erg.
1J=10⁷ erg
In MKS and SI system, unit of work is N-m or J.
If the direction of force is towards the center of the circle and direction of motion is along the tangent to the circle at that point and perpendicular to the direction of force. Then, work done is zero.
Energy
Capacity of doing work is called energy because work is done by transtormation of energy, so unit of work and energy is same i.e., joule.
There are many types of energy, such as
(i) Mechanical energy
(ii) Chemical energy
(iii) Solar energy
(iv) Nuclear energy
(v) Light energy
There are two types of mechanical energy
Kinetic Energy
The energy of a body by virtue of its motion, is called kinetic energy. If a body of mass m is moving with velocity v, then kinetic energy
=1/2mv²
If the momentum of the body is p, then kinetic energy
= p²/2m
Potential Energy
The energy of a body by virtue of its position or/and configuration is called potential energy.
Potential energy = mgh
Total Mechanical Energy
The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of a body or system is known as its total mechanical energy.
Conservation of Total Mechanical Energy
If there is no external force on a body and there is no dssipative force, then total mechanical energy of a body or system will remain conserved.
According to this law, "energy can neither created nor be destroyed, but one form of energy can be converted into another form".
Work Energy Theorem
It states that sum of work done by all the forces acting on a body is equal to its change in kinetic energy.
Power
Rate of doing work is called power. It is a scalar quantity.
Power, P = Work /Time = W/T
P = F • v
Unit of power is watt.
Some other units of power
1 kilowatt =10³ watt
1 mega watt = 106 watt
1 horse power = 746 watt
Important TIPS
- If displacement is perpendicular to the direction of force, then work done is zero.
- If a body is moving on a circle, then after completing cycle, work done is zero.
- Work done does not depend on the path followed and time taken.
- W = 1/2 mv²2 – 1/2 mv²1 (Work Energy Theorem)
- When the body is projected upwards, then its kin energy goes on changing into potential energy.
- When a body is falling downward then its potential energy goes on changing into kinetic energy.
Related Questions : (Answer in comment box.)
Q1. If the power of any engine is 1HP, then what does it means?
(a) Engine work for 746 N
(b) The rate of doing work by the engine is 746 J/s
(C)Total work done by the engine is 746 J
(d) None of the above
Q2. One "horse power" is equal to
(a) 750 W
(b) 746 W
(c) 775 W
(d) 760 W
Q3. The relation between kinetic energy K and linear momentum p of a particle is represented by
(b) 2K² = mp
(d) 2mK = P
(c) K² = 2mp
(d) p² = 2mk
Q4. An artificial satellite is revolving around earth. The physical quantity which is conserved is
(a) angular momentum
(b) moment of inertia
(c) torque
(d) total energy
Q5. Maximum work will be done if the angle between force applied and displacement produced is
(a) zero
(b) 90°
(c) 45°
(d) 180°
Q6. Minimum work will be done if the angle between the impressed force and displacement caused is
(a) 90°
(b) 60°
(c) 45°
(d) zero
Q7. A body of mass M1 Collides with another mass M2 at rest. The collision is elastic. Maximum transfer of energy Occurs when
(a) M1 = M2
(b) M1 < M2
(c) M1 > M2
(d) None of these
Q8. The bullet is fired from the rifle and the rifle recoils. The kinetic energy of the rifle is
(a) less than KE of bullet
(b) greater than KE of bullet
(c) None of these
(d) equal to KE of bullet
| Work, Energy and Power |

0 Comments
If you have any doubts let me know.